
- #SEATTLE ALASKA QUAKE PROFESSIONAL#
- #SEATTLE ALASKA QUAKE TV#
Plafker spent most of the summer in Alaska researching and documenting the earthquake. Ned Rozell’s personal account of his meeting with George Plafker, one of three USGS Geologists who responded to the Alaska quake a few days after event. Alaska Science Forum: Feet on the Ground Right After Alaska’s Big One.
#SEATTLE ALASKA QUAKE TV#
Produced by Creative Arts Studio in 1964 for the USGS.Įxcerpt from the TV show “The Big Picture” produced by the US Army in 1966 about the Alaska Earthquake and its tragic effects.
#SEATTLE ALASKA QUAKE PROFESSIONAL#
These films were shot by amateur and professional cameramen in the hours and days following the earthquake at locations such as Anchorage, Kodiak, Seward, Valdez, Chenega, Afognak.Īn examination of the 1964 Alaska Good Friday Earthquake from a (pre- plate tectonics theory) geological point of view.
Clips of the Alaska Earthquake from The Alaska Film Archives. Includes extensive archival footage of the earthquake and aftermath. Military, and local, state, and federal officials. 
This “Story map” combines an interactive map with historic photos of the earthquake.Ī documentary chronicling the first 72 hours after the 1964 Alaska Earthquake and the response to the disaster by the United States Office of Civil Defense, U.S. 1964 Alaska Earthquake Photo Tour of Anchorage.

Explains how Yakutat terrane accretion drives mountain building and crustal fault earthquakes like the 2002 M7.9 Denali Earthquake.
Tectonics & Earthquakes of Alaska-More than just plate boundariesĪn animation that describes earthquakes along the Aleutian subduction zone, one of the most seismically active in the world, and the Queen Charlotte Transform Fault. Tsunamis Generated by Megathrust EarthquakesĪn animation about tsunami-generating megathrust earthquakes using examples from Japan (2011), Chile (2010), and Alaska (1964) to describe structures that generate deadly tsunamis including: megathrust plate-boundary displacement, deformation of the overriding plate by splay faulting and/or folding, and earthquake-generated landslides. Animations explain the magnitude (Just how big is 9.2?), rupture processes, elastic rebound, and resulting tsunami. Butler explaining the science behind the earthquake. The 1964 Alaska Earthquake-What Happened and Why. “The 1964 Alaska Earthquake and Tsunami” lecture by George Plafker, USGS Geologist Emeritus. This was a great leap forward in resolving key mechanisms of the developing theory of plate tectonics.Īn expanded version (11 min) is also available: 1964 Quake: The Alaska Earthquake The video features USGS geologist George Plafker who, in the 1960’s, correctly interpreted the quake as a subduction zone event. history had profound and lasting impacts on our lives. Short video (4 min) by Stephen Wessells, USGS relating how the largest quake in U.S. Magnitude 9.2: The 1964 Alaska Earthquake. Summary of the earthquake’s cause and effects from the Alaska Earthquake Information Center. Map showing ground motion and shaking intensity based on instrumental measurements of shaking along with information about local geology and the earthquake’s location and magnitude. commemorates the Alaska Earthquake and examines the advances in knowledge and technology that have helped improve earthquake preparation and response in Alaska and around the world. The 1964 Alaska Earthquake and Tsunamis-A Modern Perspective and Enduring Legacies. United States Government Printing Office, Washington: 1993. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1527, Seismicity of the United States, 1568-1989 (Revised), Learn about the great leaps in research over the past 50 years. earthquake ever recorded, and a turning point in earth science. Science Features: The 1964 Alaska Earthquake & Tsunami. 
The map shows the epicenter of the 1964 Alaska Earthquake (red star), caused when the Pacific Plate lurched northward underneath the North American Plate. It is also the second largest earthquake ever recorded, next to the M9.5 earthquake in Chile in 1960. The earthquake lasted approximately 4.5 minutes and is the most powerful recorded earthquake in U.S. The earthquake rupture started approximately 25 km beneath the surface, with its epicenter about 6 miles (10 km) east of the mouth of College Fiord, 56 miles (90 km) west of Valdez and 75 miles (120 km) east of Anchorage. On Maat 5:36pm local time (March 28 at 3:36 UTC) an earthquake of magnitude 9.2 occurred in the Prince William Sound region of Alaska.
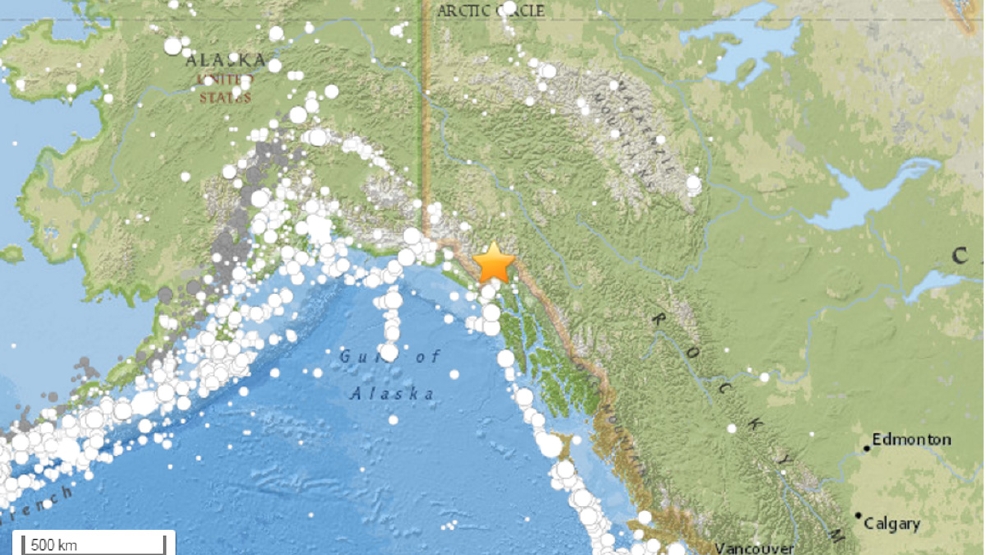
Map of southern Alaska showing the epicenter of the 1964 Alaska Earthquake (red star).








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
